Physiology II

Electronic III
The aim of this course to improve the knowledge in the fundamentals of Electronic Engineering in the most simple, effective and fast way. This course will focus on Oscillator amplifier Hartley oscillator Mono stable MTV and so on.
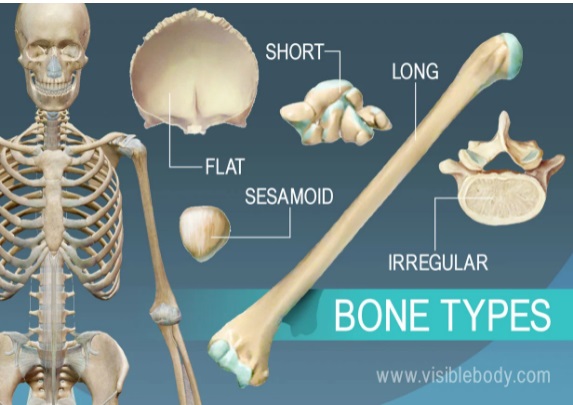
Bone Injury and Fractures
A bone fracture is a broken in bone that it can range from a thin crack to a complete break. Bone can fracture crosswise, lengthwise, in several places, or into many pieces. Most fractures happen when a bone is impacted by more force or pressure than it can support. Most fractures are accompanied by intense pain when the initial injury occurs. It may become worse when you move or touch the injured area. In some cases, you may even pass out from the pain. You may also feel dizzy or chilled from shock.
Numerical Analysis
Numerical analysis is the area of mathematics and computer science that creates, analyzes, and implements algorithms for solving numerically the problems of continuous mathematics.
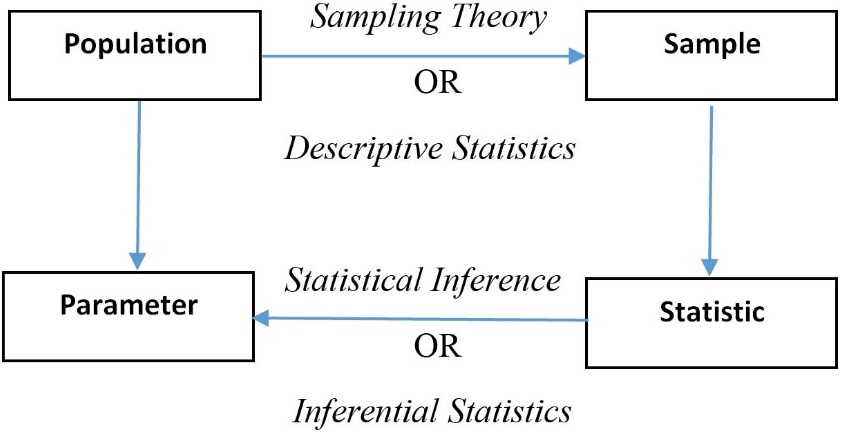
Engineering Statistic
Statistics is the science concerned with developing and studying methods for collecting, analyzing, interpreting and presenting empirical data. Statistics is a highly interdisciplinary field; research in statistics finds applicability in virtually all scientific fields and research questions in the various scientific fields motivate the development of new statistical methods and theory. In developing methods and studying the theory that underlies the methods statisticians draw on a variety of mathematical and computational tools.