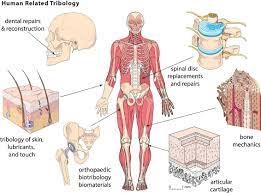
Biotribology
Biotribology :
The application of tribology in biology is a growing and rapidly expanding field. It
necessarily builds upon the fundamentals of engineering tribology and extends well
beyond conventional boundaries.
Biomedical tribological systems involve an extensive range of synthetic materials and
natural tissues, which often operate in complex interactive biological environments. Their
performance specifications and lifetimes often exceed that found in many engineering
systems and frequently have to extend beyond the lifetime of the patient. Biomedical
tribology involves natural human and animal systems and, of increasing importance, the
development of replacement (prosthetic) devices to replace diseased tissues and organs.
The current designs of prosthetic devices, such as total replacement joints, have
demonstrated clinical lifetimes of well beyond 10 years. These successes have also led to
new types of problems, relating to long-term tribological and biological interactions within
the human body that can limit the lifetime of many of these devices. As the average age of
the elderly population increases, their expectations of levels of activity and quality of life
increase, the fundamental specification and long-term performance requirements of
biomaterials and prosthetic devices are being extended.
A new era of biotribology is now emerging, in which the conventional approach of
defining tribological requirements in terms of engineering functions is no longer adequate.
The course focuses on the major areas of tribology and, primarily, biotribology, the natural
human joints, and their artificial replacements. The natural synovial joint and artificial
cartilages are initially described. The types of joint replacements are introduced and the
major limitations that control their long-term survivorship in patients and adverse
biological reactions are discussed.
Finally, the alternatives for joint replacement in the next millennium are described,
including both functional biomaterials that are engineered to give improved biological
activity and viable tissue-engineered systems.
Biotribology is an area that concerns itself with tribology its applications to biomechanics,
biomaterials, orthopedics, and other biological systems. It can be defined as the study of
biological processes.
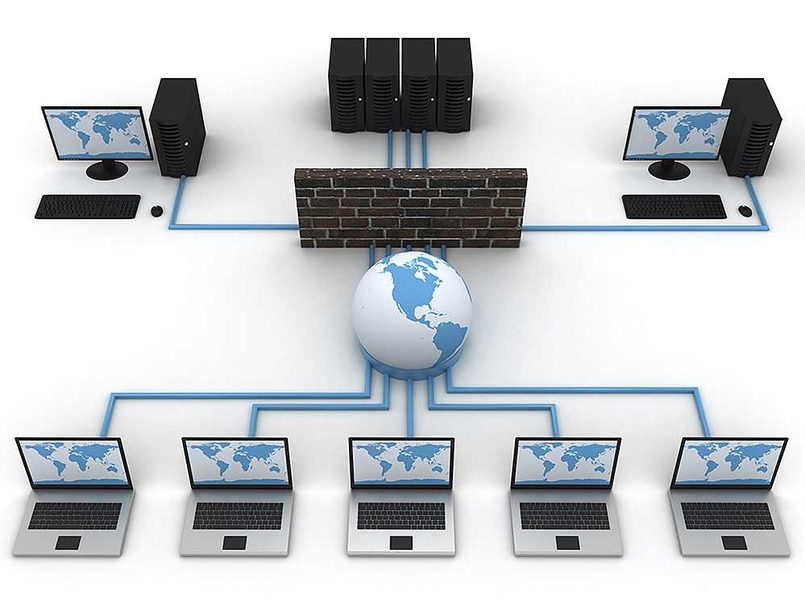
Computer Network
This course provides an introduction to computer networks, with a special focus on the Internet architecture and protocols. Topics include layered network architectures, addressing, naming, forwarding, routing, communication reliability, the client-server model, web and email protocols.
Signal & System
Digital signal processing (DSP) technology and its advancements have dramatically impacted our modern society everywhere. Without DSP, we would not have digital/Internet audio or video; digital recording; CD, DVD, and MP3 players; digital cameras; digital and cellular telephones; digital satellite and TV; or wire and wireless networks.
Medical instruments would be less efficient or unable to provide useful information for precise diagnoses if there were no digital electrocardiography (ECG) analyzers or digital x-rays, medical image systems (MRI) , electroencephalogram (EEG) ... etc.
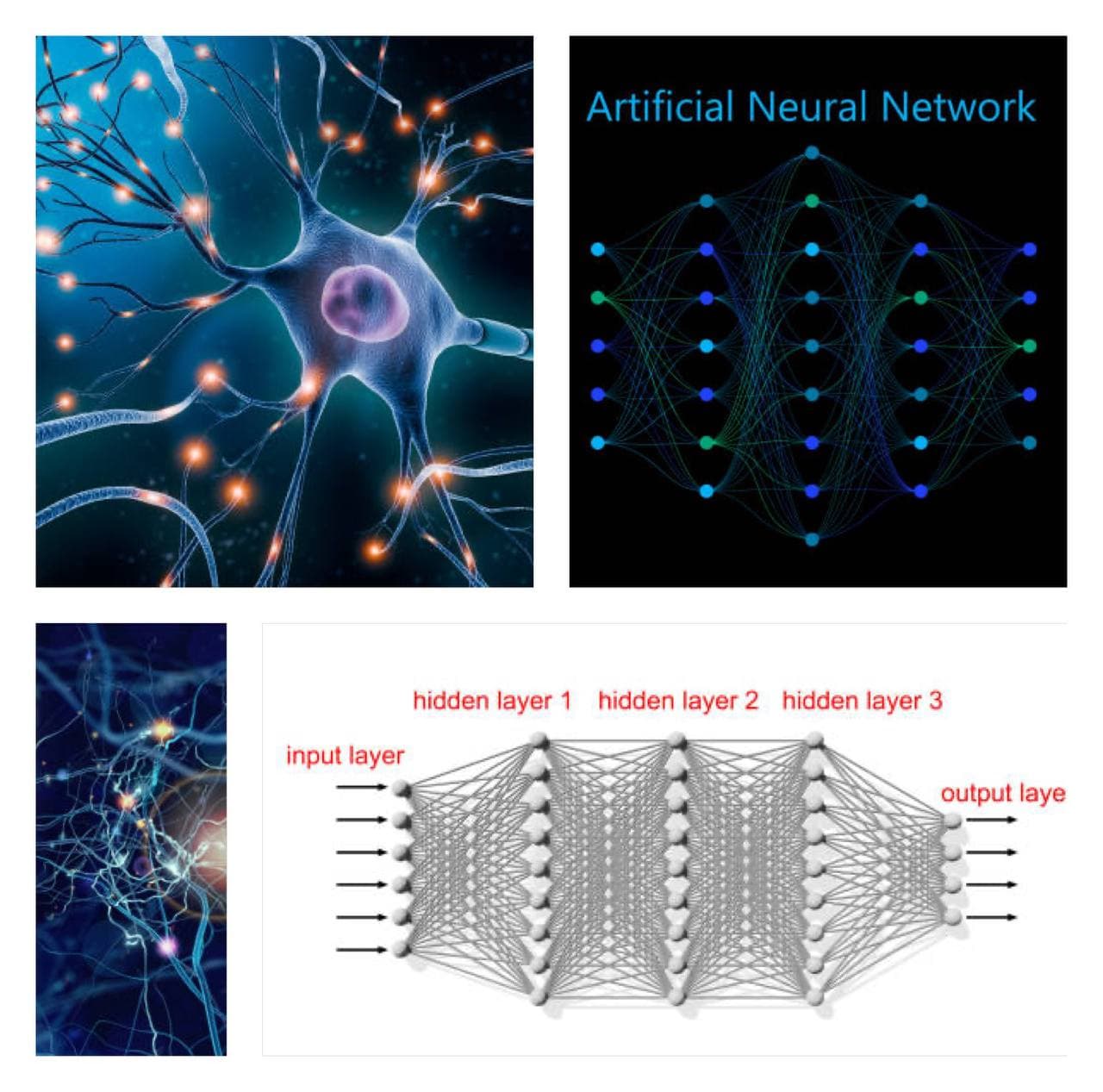
Neural Networks
An artificial neuron network (neural network) is a computational model that mimics the way nerve cells work in the human brain. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) use learning algorithms that can independently make adjustments - or learn, in a sense - as they receive new input. This makes them a very effective tool for non-linear statistical data modeling.
Electromechanical Design
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), such as pressure sensors, accelerometers, and bio-mechanical assemblies and displays, require knowledge of a broad range of disciplines, from microfabrication to electromechanical. This subject presents an introduction to this broad field, using examples and design projects drawn from real MEMS and Bio-MEMS applications.
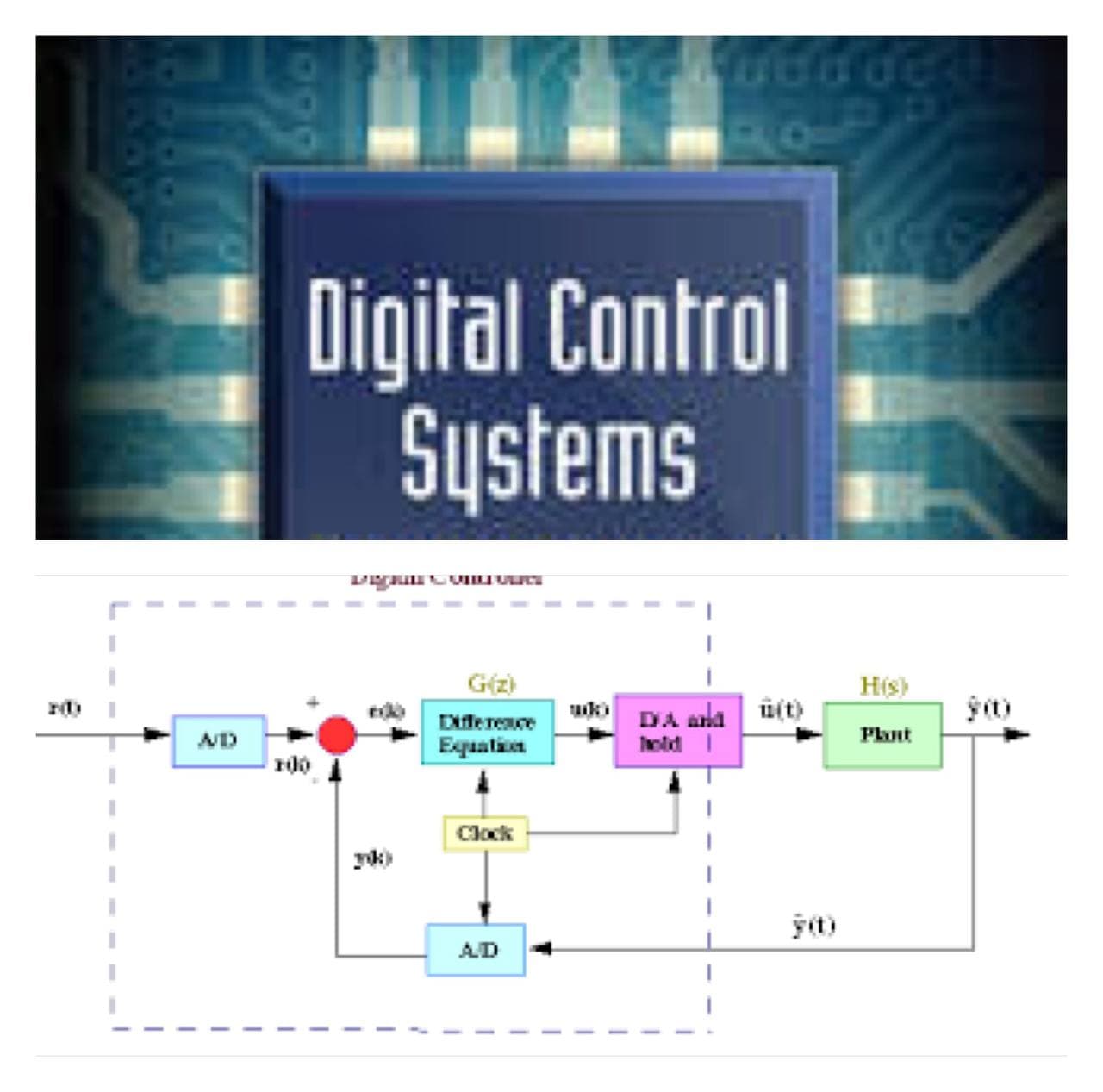
Control II
When computers came onto the scene, their obvious applicability to control soon became apparent, and digital control systems started to appear. A digital control system is a control system that processes signals coming from sensors by means of a computer. The analog signal (continuous in value and time) has to be sampled and take discrete values at given time intervals. This process is known as signal digitalization.

Biomedical Sensors
The sensors are devices that can transform non-electrical signals into electrical
signals. The biomedical sensor is a very important kind of sensors. First we will
introduce some basic knowledge about biomedical sensors including a definition
and classification.
