Arabic Language 4 - E
تحتلُّ اللغة العربية مكانةً مرموقة بينَ لغات العالم، بل هي أشرفُ اللغات وأكثرها تميزًا، حَسبُها أنّها لغة القرآن الكريم ولغةُ أهل الجنة، وفيها من السحر والبيان ما لا يوجد في أي لغةٍ أخرى، وبالإضافة إلى جمالها وسحرها فإنها من أكثر اللغات انتشارًا في العالم، ويتحدّث بها عددٌ كبيرٌ من الناس في مختلف بقاع العالم وليس في الوطن العربي فقط، وتُعدّ اللغة العربية من أكثر اللغات غزارةً من حيث المادة اللغوية، كما أنها من اللغات الحية التي تضم مفرداتٍ كثيرة ومترادفاتٍ لا يوجد مثلُها في لغةٍ أخرى

Steel Structure Design II - E
Structural steel is steel construction material which fabricated with a specific shape and chemical composition to suit a project's applicable specifications.In modern construction, steel structures is used for almost every type of structure including heavy industrial building, high-rise building, equipment support system, infrastructure, bridge, tower, airport terminal, heavy industrial plant, pipe rack, etc.Because of the high strength grade of steel, this structure is reliable and requires less raw materials than other types of structure like concrete structure and timber structure.Depending on each project’s applicable specifications, the steel sections might have various shapes, sizes and gauges made by hot or cold rolling, others are made by welding together flat or bent plates. Common shapes include the I-beam, HSS, Channels, Angles and Plate. American Institute of Steel Construction Manual (AISC) will be used in this course,
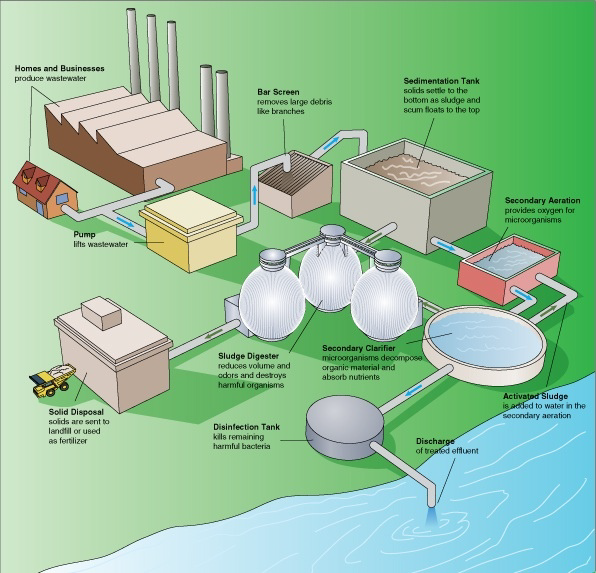
Sanitary and Environmental Engineering II - E
Sanitary Engineering course aims at providing the students with a complete knowledge on wastewater collection, conveyance, treatment, disposal methods and design. This course will introduce the principles and practices of wastewater and storm-water collection systems. Sewer design issues, the hydraulic design of gravity and pressure sewers, sewer system layout, appurtenances and structural design of sewer lines will be discussed. In addition, an introduction to wastewater and sludge treatment will be provided. After completing the course, the students are expected to solve the problems of wastewater, quantify quantities of storm water using various methods, explain physical, chemical and biological characteristics of sewage and design of wastewater collection system.

Reinforced Concrete Design IV - E
In this semester, we will discuss the methods of designing and analyzing slabs with different shapes by using yield line theory, where the student will be able to design and analyze different shapes of slabs. We will also deal with the subject of prestress beams and how to design and analyze this type of important and frequently used structural member in bridges. Finally, we will address the subject of stairs, where the student will be able to design stairs and learn how to reinforce them.
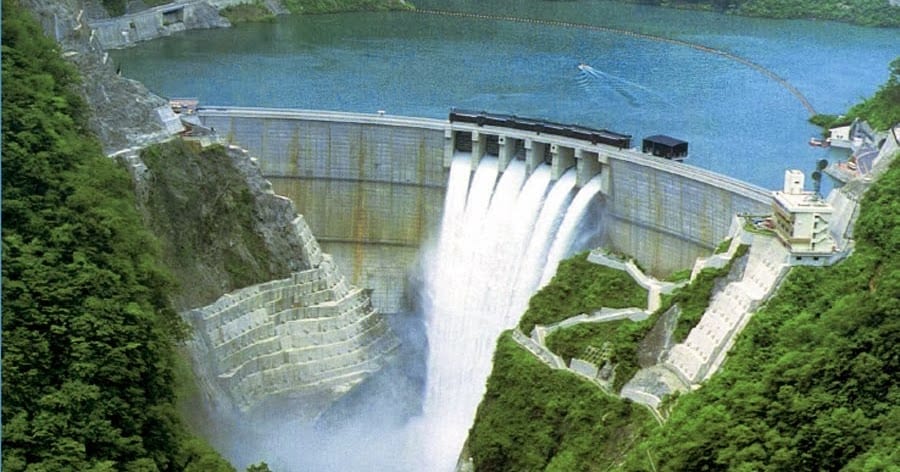

Hydraulic Structures II - E
A hydraulic structure is a structure submerged or partially submerged in any body of water, which disrupts the natural flow of water. They can be used to divert, disrupt or completely stop the flow. An example of a hydraulic structure would be a dam, which slows the normal flow rate of the river in order to power turbines. A hydraulic structure can be built in rivers, a sea, or any body of water where there is a need for a change in the natural flow of water.
Hydraulic structures may also be used to measure the flow of water. When used to measure the flow of water, hydraulic structures are defined as a class of specially shaped, static devices over or through which water is directed in such a way that under free-flow conditions at a specified location (point of measurement) a known level to flow relationship exists. Hydraulic structures of this type can generally be divided into two categories: flumes and weirs.

Highway Engineering II- E
Outline Description of Module
This module introduces students to cover:
Knowledge and Understanding
Having successfully completed this module, a student will be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of:

Foundation Engineering Design II - E
Course Description
The course consists of four parts deals with the design and analysis of deep foundations (pile foundations), lateral earth pressure of the soil, design and analysis of sheet piles and retaining walls.
Prerequisites
Soil Mechanics I, Soil Mechanics II. and Foundation Engineering I
Textbook
· Principles of Foundation Engineering, Braja Das, ninth Edition 2019.
· Foundation Analysis and Design by Joseph E. Bowles (1982)
· Foundation design and Construction by Tomlinson (2006)
Course Objectives
Objective 1: Study the load capacity of pile foundations.
Objective 2: Study the lateral earth pressure of the soil.
Objective 3: Study the sheet piles.
Objective 4: Study the retaining walls.
Specific Learning Outcomes
Specific Learning Outcomes for Objective 1:
· Design and analysis of pile foundations.
Specific Learning Outcomes for Objective 2:
· Calculate the lateral earth pressure of the soil.
Specific Learning Outcomes for Objective 3:
· Design and analysis of sheet piles.
Specific Learning Outcomes for Objective 4:
· Design and analysis of retaining walls
Topics
1. Pile foundations:
Pile classification, pile capacity in cohesive soils, pile capacity in cohesionless soils, pile capacity for c-ϕ soils, pile capacity of tension piles, determination of pile capacity from in situ tests, negative skin friction of piles.
2. Pile groups:
· Group action, efficiency of group piles, ultimate bearing capacity of group piles, pile groups subjected to moments, settlement of pile groups.
· pile dynamic formulae
· pile load tests
3. Earth pressures and retaining walls:
Types of lateral earth pressures, Rankine theory of earth pressures, Coulomb’s theory of earth pressures.
4. Stability of retaining walls
· Sheet piles:
Cantilever sheet pile walls and anchored sheet pile walls
Class/Laboratory Schedule:
Saturday 14:30 – 16:30 ; Monday 14:30 – 16:30
Fifteen weeks’ summer class
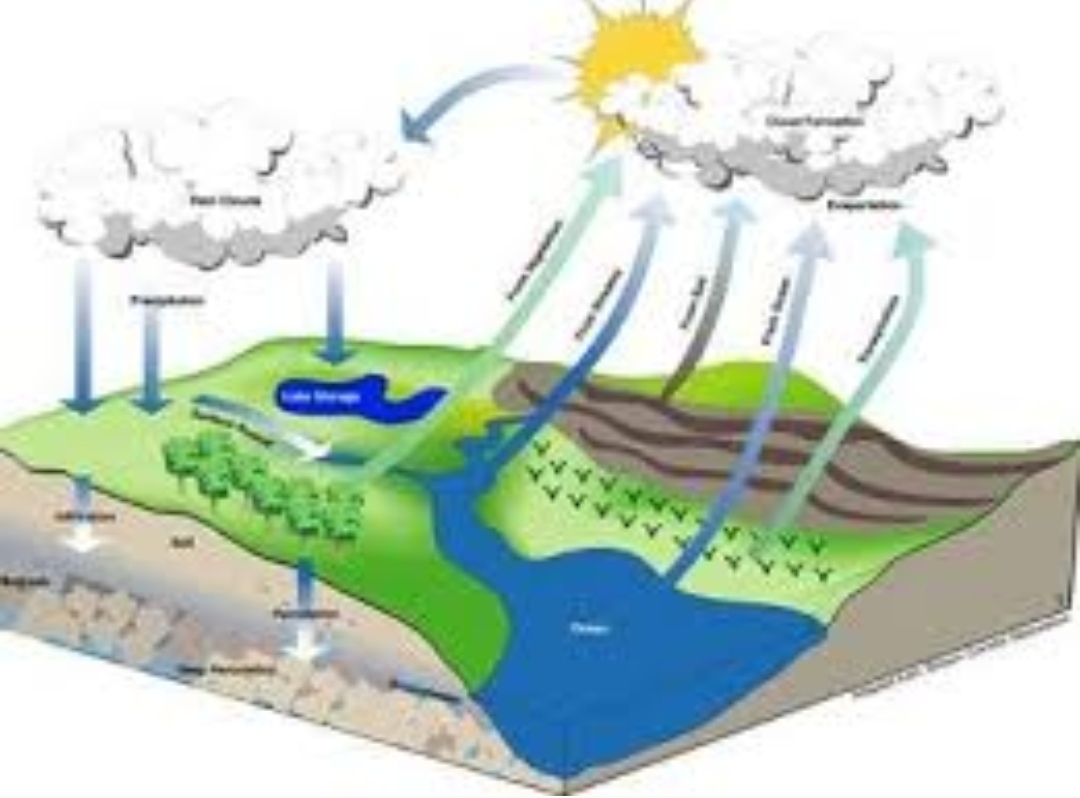
Engineering Hydrology II -E
Hydrology is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability

