
Construction Methods and Quantity Surveying I - E
Construction Methods and Estimating (Quantity Surveying)
Syllabus:
1- Reducing Project Duration (Crush Program)
2- Construction Equipments
3- Classification of Construction Equipments
4- Sources of Construction Equipments
5- Cost of Owning and Operating Construction Equipments
6- Engineering Fundamentals of moving earth
7- Productivity of Equipments
8- Concrete and Concrete Equipments
9- Soil Compaction
10-Estimating
11-Approximate Estimating
12-Detailed Estimating
13-Bill of Quantities
14-The Quantity of reinforced steel in concrete
15-Construction Works analysis in to materials
16-الشروط العامة للمقاولات (اعمال الهندسة المدنية)
17- Specifications
References
1- Construction Planning , Equipment , and Methods ( L. Peurifoy)
2- Estimating in Building Construction (J. Peterson and R. Dagostion)
3- Estimating and tendering for construction work (Martin Brook)
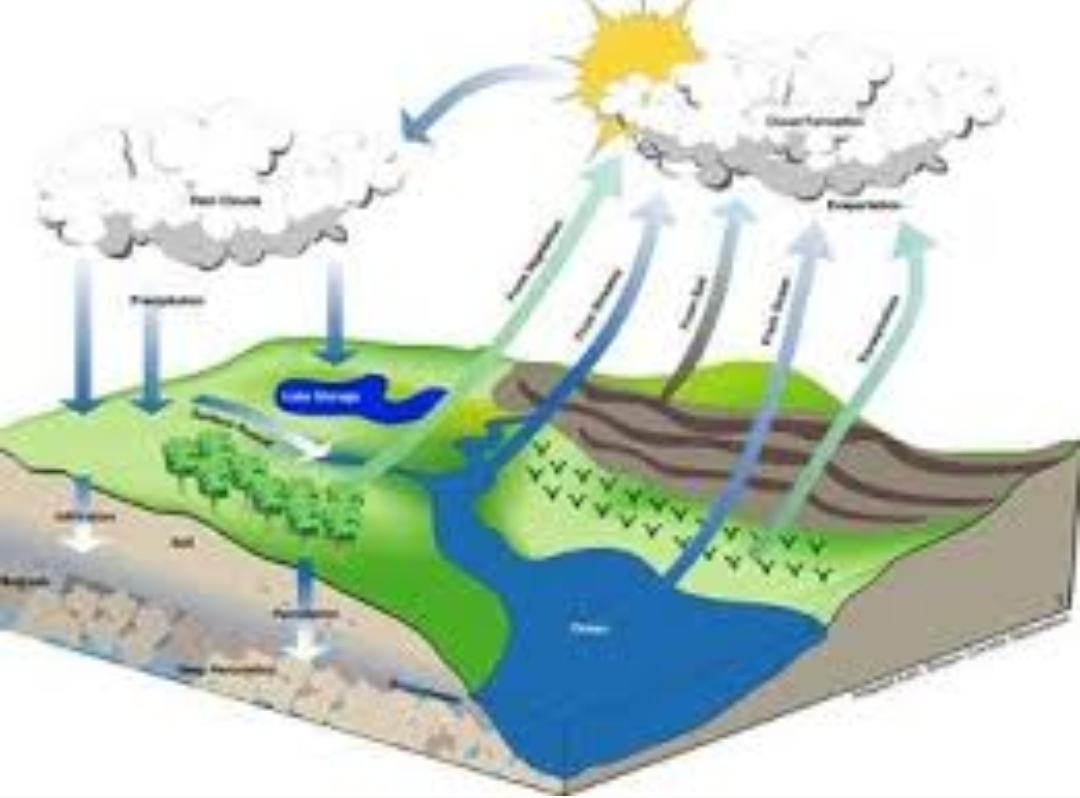
Engineering Hydrology I -E
Hydrology is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability

Foundation Engineering Design I - E
Course Description
The course consists of five parts dealing with the analysis and design of foundations; soil investigation, bearing capacity of shallow foundation, settlements of shallow foundations, and foundations on difficult soils. Structural design and determination of dimensions of footings.
Prerequisites
Soil Mechanics I and Soil Mechanics II.
Textbook
Principles of Foundation Engineering, Braja Das, Seventh Edition 2011.
Course Objectives
Objective 1 : Study the Soil investigation.
Objective 2: Study the bearing capacity of shallow foundations.
Objective 3: Study the settlements of shallow foundations.
Objective 4: Study the foundations on difficult soils.
Objective 5: Study the Structural design and determination of dimensions of footings.
Specific Learning Outcomes
Specific Learning Outcomes for Objective 1:
· Determination of the spacing, number of boreholes and depth of boreholes.
Specific Learning Outcomes for Objective 2:
· Calculate the bearing capacity of shallow foundations.
Specific Learning Outcomes for Objective 3:
· Calculate the settlements of shallow foundations.
Specific Learning Outcomes for Objective 4:
· Understanding the behavior of foundations on difficult soils.
Specific Learning Outcomes for Objective 5:
1. Design the dimensions of footing.
2. Structural design of shallow foundations.

Highway Engineering I - E
Outline Description of Module
This module introduces students to cover:
- The technical details of highway engineering
- Earthwork and mass haul diagram
- Soil eng. for Highway Design
- Pavement types
- Pavement materials
- Pavement layers
Knowledge and Understanding
Having successfully completed this module, a student will be able to demonstrate knowledge and understanding of:
- Demonstrate an understanding of the need for developing highway engineering.
- Outline the behaviour of soils beneath pavement structures.
- Outline the fundamental behaviour of paving materials.
- Outline the principal means of mixture design.
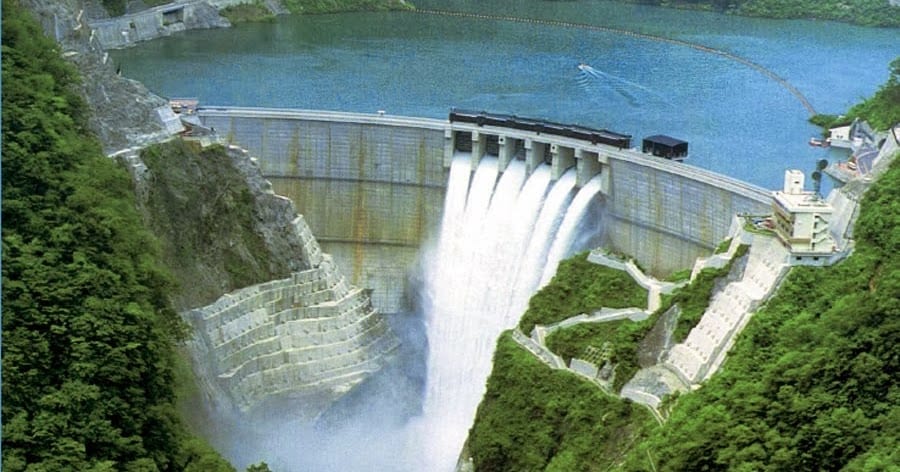

Hydraulic Structures I - E
A hydraulic structure is a structure submerged or partially submerged in any body of water, which disrupts the natural flow of water. They can be used to divert, disrupt or completely stop the flow. An example of a hydraulic structure would be a dam, which slows the normal flow rate of the river in order to power turbines. A hydraulic structure can be built in rivers, a sea, or any body of water where there is a need for a change in the natural flow of water.
Hydraulic structures may also be used to measure the flow of water. When used to measure the flow of water, hydraulic structures are defined as a class of specially shaped, static devices over or through which water is directed in such a way that under free-flow conditions at a specified location (point of measurement) a known level to flow relationship exists. Hydraulic structures of this type can generally be divided into two categories: flumes and weirs.
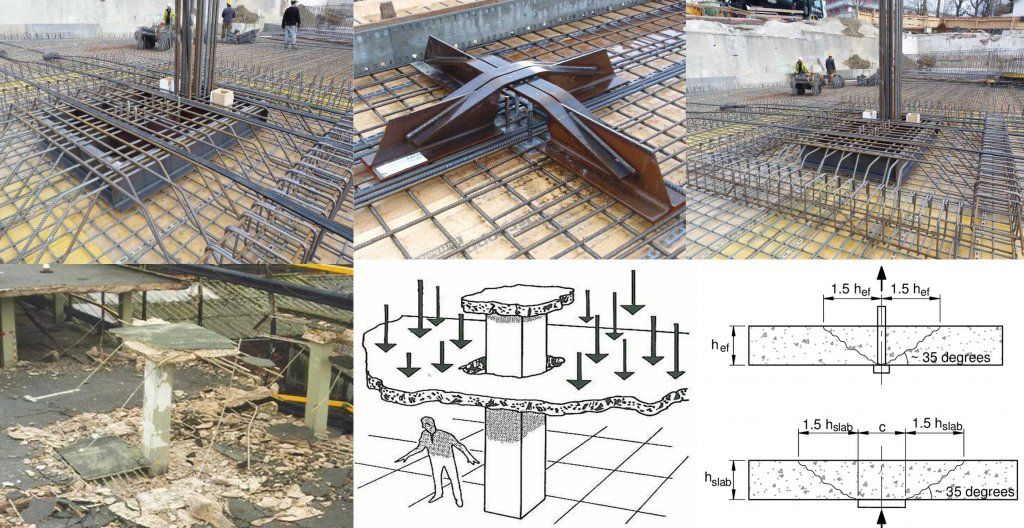
Reinforced Concrete Design III - E
In this semester, we will discuss the methods of designing slabs, where the student will be able to design and analyze different types of slabs in more than one way, in addition to knowing and designing slabs to resist punching shear. We will also deal with the subject of prestress beams and how to design and analyze this type of important and frequently used structural member in bridges. Finally, we will address the subject of structures where the student will be able to design as well as learn how the loads and moments are transferred between the different structural members.
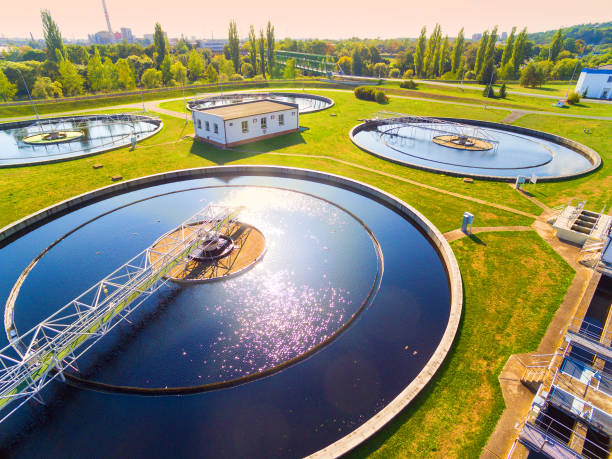

Sanitary and Environmental Engineering I - E
Environmental and Sanitary Engineering is a profession that involves planning, design, management, construction, operation, maintenance in the fields of water supply engineering, solid waste management, sewage and wastewater engineering, environmental management and engineering, plumbing, fire protection and public health engineering all in accordance with governing laws, code of ethics and local and global technological trends and developments.
This course will introduce the principles and practices of water collection systems for various purposes, variation in rate of consumption, factors affecting consumption, fire demand, forecasting population, Water distribution systems, Collection and distribution of water, Pumps and Pumping Stations, and design of water treatment tanks.
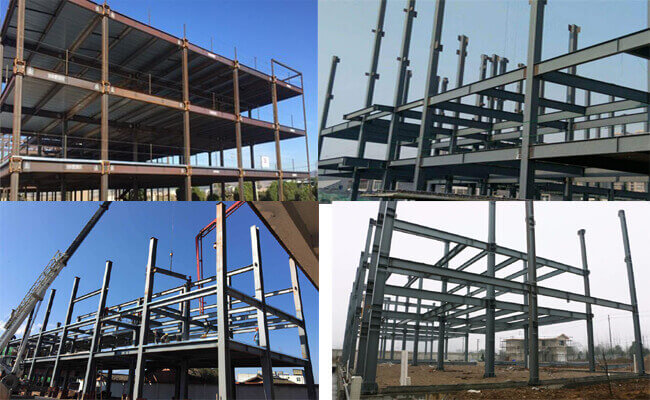

Steel Structure Design I - E
Structural steel is steel construction material which fabricated with a specific shape and chemical composition to suit a project's applicable specifications.In modern construction, steel structures is used for almost every type of structure including heavy industrial building, high-rise building, equipment support system, infrastructure, bridge, tower, airport terminal, heavy industrial plant, pipe rack, etc.Because of the high strength grade of steel, this structure is reliable and requires less raw materials than other types of structure like concrete structure and timber structure.Depending on each project’s applicable specifications, the steel sections might have various shapes, sizes and gauges made by hot or cold rolling, others are made by welding together flat or bent plates. Common shapes include the I-beam, HSS, Channels, Angles and Plate. American Institute of Steel Construction Manual (AISC) will be used in this course,