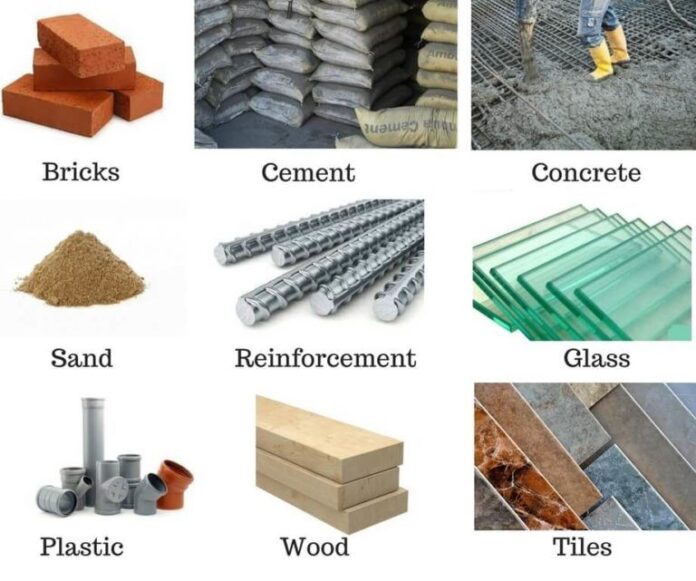

Construction Materials I - E
A building material is any material which is used for a construction purpose. Apart from naturally occurring materials, many man-made products are in use.
Materials that are used in the building construction such as cement, brick, wood, glass and concrete, ...etc., are called building materials.
The engineers and the builders must all understand building materials performance under several conditions such as load, heat, weather, ...etc, to use it to the best advantage.

Electrical Engineering - E
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use.
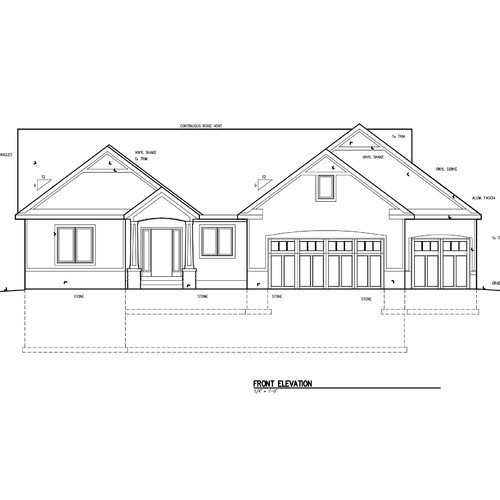
Engineering Drawing I -E
An engineering drawing is a subcategory of technical drawings. The purpose is to convey all the information necessary for manufacturing a product or a part.
Engineering drawings use standardised language and symbols. This makes understanding the drawings simple with little to no personal interpretation possibilities.

Engineering Mechanics I - E
This course starts with an introduction that covers the fundamental concepts
and principles of Statics. The equilibrium of particles is then introduced
along with the rules of adding and subtracting force vectors. The course
then proceeds to cover the equilibrium of rigid bodies in two and three
dimensions and the analysis of different types of structures and
machines. Determination of the moment of a force about an arbitrary point
and/or axis, the equivalence of a system of forces and/or couples to the
Resultant Force and/or Couple will also be introduced.

Engineering Statistics I - E
Statistics is the science concerned with developing and studying methods for collecting, analyzing, interpreting and presenting empirical data. Statistics is a highly interdisciplinary field; research in statistics finds applicability in virtually all scientific fields and research questions in the various scientific fields motivate the development of new statistical methods and theory. In developing methods and studying the theory that underlies the methods statisticians draw on a variety of mathematical and computational tools.
Two fundamental ideas in the field of statistics are uncertainty and variation. There are many situations that we encounter in science (or more generally in life) in which the outcome is uncertain. In some cases the uncertainty is because the outcome in question is not determined yet (e.g., we may not know whether it will rain tomorrow) while in other cases the uncertainty is because although the outcome has been determined already we are not aware of it (e.g., we may not know whether we passed a particular exam).
Probability is a mathematical language used to discuss uncertain events and probability plays a key role in statistics. Any measurement or data collection effort is subject to a number of sources of variation. By this we mean that if the same measurement were repeated, then the answer would likely change. Statisticians attempt to understand and control (where possible) the sources of variation in any situation.
We encourage you to continue exploring our website to learn more about statistics, our academic programs, our students and faculty, as well as the cutting-edge research we are doing in the field.

English Language I - E
English I: This course emphasizes the fundamental language skills of reading, writing, speaking, listening, thinking, viewing and presenting. An emphasis on vocabulary and composition skills will be an on-going part of the program. The course includes studies of various literary genres: short story, poetry, novel, drama, and non-fiction. The development of critical reading and writing skills is a major emphasis of the course.

Human Rights - E
حقوق الإنسان هي المبادئ الأخلاقية أو المعايير الاجتماعية التي تصف نموذجاً للسلوك البشري الذي يُفهم عموما بأنه مجموعة من الـحقوق الأساسية التي لا يجوز المس بها وهي مستحقة وأصيلة لكل شخص لمجرد كونها أو كونه إنسان، فهي ملازمة لهم بغض النظر عن هويتهم أو مكان وجودهم أو لغتهم أو ديانتهم أو أصلهم العرقي أو أي وضع آخر. وحمايتها منظمة كحقوق قانونية في إطار القوانين المحلية والدولية.

Mathematics I - E
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.

Programming I - E
Computer programming is the process of accomplishing a specific computing result or to perform a particular computing task, usually by designing/building an executable computer program. Programming involves tasks such as analysis, generating algorithms, profiling algorithms' accuracy and resource consumption, and the implementation of algorithms in a chosen programming language (commonly referred to as coding). The source code of a program is written in one or more languages that are intelligible to programmers, rather than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. The purpose of programming is to find a sequence of instructions that will automate the performance of a task (which can be as complex as an operating system) on a computer, often for solving a given problem. Proficient programming thus usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the application domain, specialized algorithms, and formal logic